Computer Networks - Introduction
In this blog, I have discussed the beginning of the internet and some terms related to computer networks.
Table of contents
- What is Internet?
- Begining of Internet
- Origin of World Wide Web
- What are Network Topology?
- Types of Topologies
- 1. Bus Topology
- Advantages of Bus Topology:-
- Disadvantages of Bus Topology:-
- 2. Ring Topology
- Advantages of Ring Topology:-
- Disadvantages of Ring Topology:-
- 3. Star Topology
- Advantages of Star Topology:-
- Disadvantages of Star Topology:-
- 4. Mesh Topology
- Advantages of Mesh Topology:-
- Disadvantages of Mesh Topology:-
- Some Terms related to Computer Networks:-
- Thank you.
What is Internet?
The Internet is the global/worldwide interconnected network of devices which allows the user of a respective device to access the information from other devices or transfer the data from one device to other device.
ICANN (The Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Network) is a non-profit organization based in United States which is responsible for maintaining Internet.
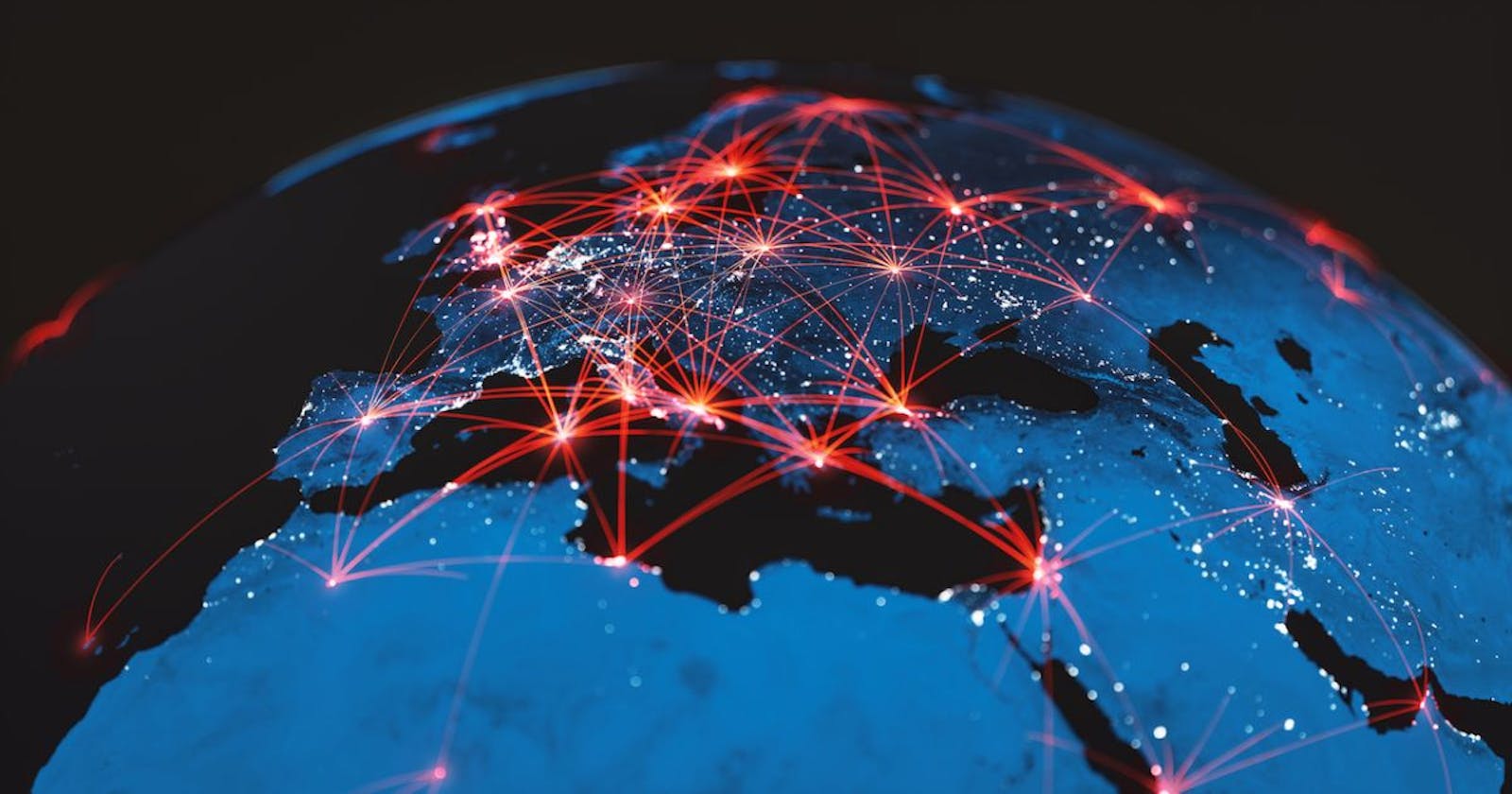
The internet travels through the cable and they connect the whole world through these cables under the sea. You can checkout this link which shows you the cables under the sea of around the world:- Click Here
A demo image of under water cables around the world is given below.
Begining of Internet
It was time of the Cold War where the United States and Soviet Union were fighting over who is more powerful. On 1957, during Cold War, Soviet Union launched Sputnik, the first ever man-made satellite. The news shocked the Americans.
In the year 1958 Americans created the ARPA (Advanced Research Projects Agency) in the response to the Sputnik launch. The purpose of the ARPA was to give United State an edge in the technological advancement and also had an important mission called Computer Science.
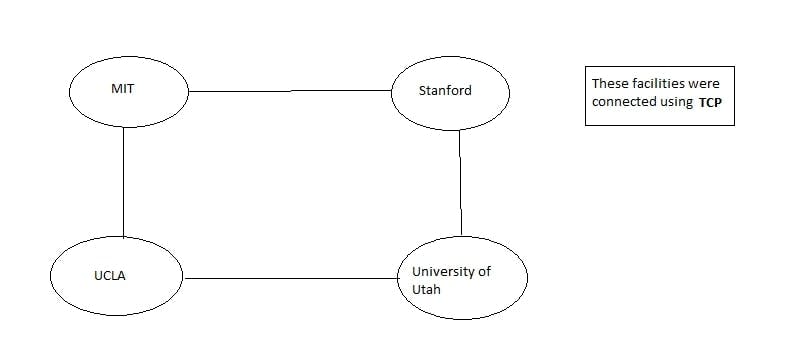
ARPA had various facilities accross United States, these facilities were MIT, Stanford, UCLA and University of Utah, containing computers and required hardwares, but they were very far away from each other. It was very difficult to stay connected from this far away. So, they introduced a network called ARPANET. Using the ARPANET the facilities were easily able to communicate with each other. It used TCP (Transmission Control Protocol), which we will look into later in detail.
Let's say you want to share a file that is very important to you and your friend. Now, to send this file from one device to another the internet is responsible for transfering this file securely. So, to send this file securely there might be some rules that are set by someone. These set rules are called Protocol, like we talked about TCP previously.
Later, in the year 1983, the Internet was officially started for the public to use. Before the official launch of Internet for public use, many researches, trails and errors were done and finally ARPA introduced the new communication protocol called TCP/IP (Transfer Control Protocol/Internetwork Protocol).
Origin of World Wide Web
There was problem faced by the various universities and institution about sharing their latest advancement through research papers around the world. So, to solve this problem World Wide Web was introduced.
Tim Berners-Lee, a British Scientist, was the one who invented World Wide Web. He worked at research organization called CERN (Conseil Européen pour la Recherche Nucléaire) i.e. European Council for Nuclear Research. He wrote his first proposal about World Wide Web in the year 1989. And by the end of the year 1990, he developed and ran the first Web server and browser up and running at CERN. Click Here to visit the first ever Website.
What are Network Topology?
Network Topology is the arrangement of nodes in a way that they can be connected to communicate with each other. Here, Nodes usually includes routers, switches and computers.
Types of Topologies
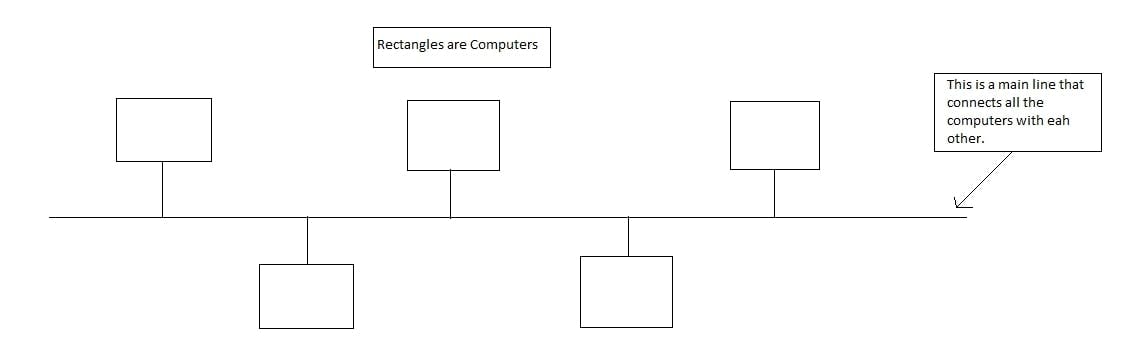
1. Bus Topology
The below image is a diagram of Bus topology. As you can see, it typically uses a long single cable/line to connect several nodes with each other in the network. The data packet sent from one node reaches another directly throught the main cable.
Advantages of Bus Topology:-
- It works well if you have to establish a small connection network.
- It is the easiest network topology for connecting computers in a linear fashion.
- It requires less cable length then Star Topology.
Disadvantages of Bus Topology:-
- It can be hard to troubleshoot each device if problem occurs.
- The whole system will go down if the something happens to main cable.
- This network topology is not favourable for large networks.
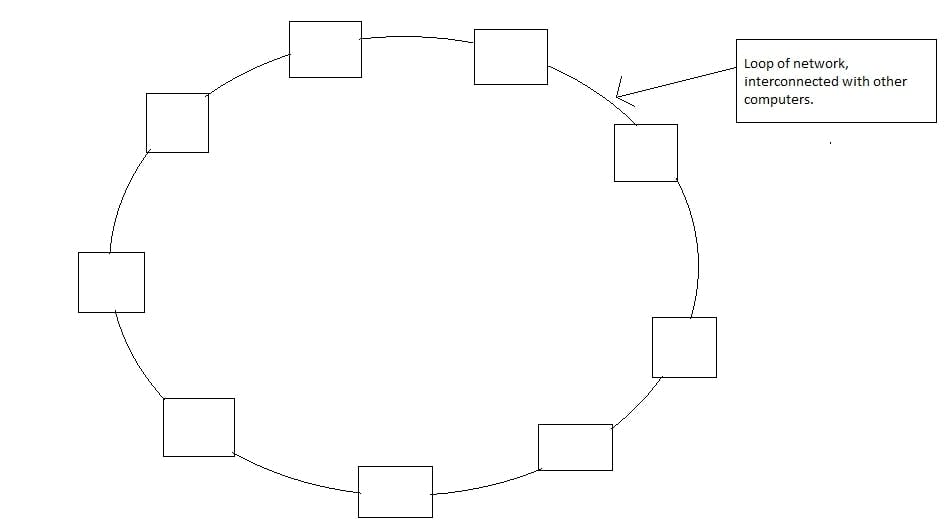
2. Ring Topology
The below image is a diagram of Ring Topology. Here, all the nodes are in an interconnected network of loop. When the data packet is sent from one node it has to travel in one direction through every device until it reaches the other node.
Advantages of Ring Topology:-
- In this network topology the data flows in one direction, so collision of data packets occur.
- It is cheap to install and expand.
- It is easy to manage.
- the speed of data transfer is very high.
Disadvantages of Ring Topology:-
- It is not scalable network connection.
- Due to uni-directional flow od data packets, the data ust pass through all the nodes.
- If one node shuts down, it affects the whole network i.e. you cannot transfer the data packet pass them.
- It is expensive
3. Star Topology
The below given image is a diagram of Star Topology. Here, all the nodes are connected to a hub in the center to form a network. The data packets travel from one node to another via that hub. This type of network is for LAN (Local Area Network).
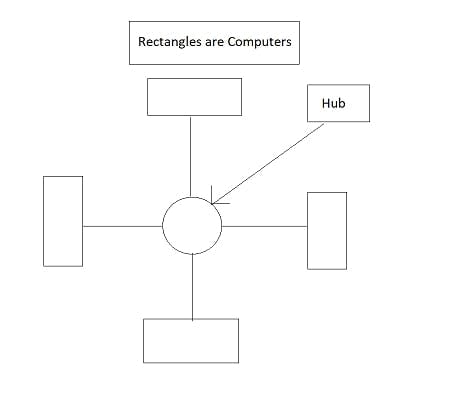
Advantages of Star Topology:-
- It is very reliable, if one node disconnects the other nodes stays connected via the hub.
- It is high-performancing as there is no collision of data packets.
- The fault detection in this network topology is very easy.
Disadvantages of Star Topology:-
- It requires more cable than bus topology.
- If the center hub goes down, the whole networ goes down with it.
- It is more expensive as external hardware (hub) is used.
4. Mesh Topology
The below given image is a diagram of Mesh Topology. Here, every single node is connected/linked with every single node via a cable. The data packets travel from nodes to nodes and there are N(N-1)/2 links in mesh if there are N nodes in this network.
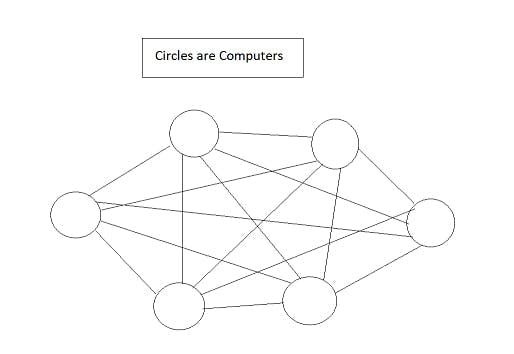
Advantages of Mesh Topology:-
- If a node shuts down or fails, the whole network will not get affected.
- The falt detection is straigthforward.
- It provides high privacy and security as the data passed directly to the destination node.
Disadvantages of Mesh Topology:-
- It is very costly when compared to other topologies.
- The setup of this network topology is very difficult.
- The maintainance is also difficult.
Some Terms related to Computer Networks:-
- LAN :- Local Area Network is for small house/office.
- MAN :- Metropolitian Area Network is for cities.
WAM :- Wide Area Network are across countries.
- There are two types of WAN:-
- SONET :- Synchronous Optical Networking
- Frame relay :- A way for you to connect LAN to WAN.
- There are two types of WAN:-
Modem :- It is something that converts digital signals into Analog/Electric signals.
- Router :- It helps to give direction to the packet based on their IP Address.
- Bridge :- It is something that creates a large network by connecting mutiple LAN.
- IP Address :- Internet Protocol Address is an id given to every device and server around the world.
- ISP :- Internet Service Provider. Example :- In India Jio, Airtel etc.
- WWW :- World Wide Web
- TCP :- Transmission Control Protocol
- UDP :- User Datagram Protocol
- HTTP :- HyperText Transfer Protocol
- OSI Model :- Open System Inter-connection Model is a model that defines the structure of network. This model is just for theoretical purpose.
- TCP/IP Model :- Internet Protocol Suite Model is a model used in today's structure of network.
- DNS :- Domain Name Server
Hope It was helpful. Stay Tuned for more.